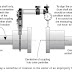
Since the images are collected in digital format, a wide variety of image manipulations are available for AFM data. Quantitative topographical information, such as lateral spacing, step height, and surface roughness are readily obtained. Images can be presented as two-dimensional or three-dimensional representations in hard copy or as digital image files for electronic transfer and publication.
Nanoindentation - A specialized probe tip is forced into the sample surface to obtain a measure of the material’s mechanical properties in regions as small as a few nanometers. (See the Handbook section on Nanoindentation Hardness Testing.)

TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
- 3-dimensional topography of IC device
- Roughness measurements for chemical mechanical polishing
- Analysis of microscopic phase distribution in polymers
- Mechanical and physical property measurements for thin films
- Imaging magnetic domains on digital storage media
- Imaging of submicron phases in metals
- Defect imaging in IC failure analysis
- Microscopic imaging of fragile biological samples
- Metrology for compact disk stampers
SAMPLE REQUIREMENTS
No sample preparation is typically required. Samples can be imaged in air or liquid. Sample height is limited to about 1.5 inches. Areas up to 8 inches in diameter can be fully traversed without repositioning. Larger samples can be fixtured for imaging within a limited area. Total surface roughness in the image area should not exceed about 6 µm.