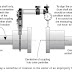
- Long tube vertical evaporators with either natural or forced circulation are most popular. Tubes are 19–63 mm dia and 12–30 ft long.
- In forced circulation, linear velocities in the tubes are 15–20 ft/sec.
- Film-related efficiency losses can be minimized by maintaining a suitable temperature gradient, for instance 40–458F. A reasonable overall heat transfer coefficient is 250 Btu/(h)(ft2).
- Elevation of boiling point by dissolved solids results in differences of 3–108F between solution and saturated vapor.
- When the boiling point rise is appreciable, the economic number of effects in series with forward feed is 4–6.
- When the boiling point rise is small, minimum cost is obtained with 8–10 effects in series.
- In countercurrent evaporator systems, a reasonable temperature approach between the inlet and outlet streams is 308F. In multistage operation, a typical minimum is 108F.
- In backward feed the more concentrated solution is heated with the highest temperature steam so that heating surface is lessened, but the solution must be pumped between stages.
- The steam economy of an N-stage battery is approximately 0.8N lb evaporation/lb of outside steam.
- Interstage steam pressures can be boosted with steam jet compressors of 20–30% efficiency or with mechanical compressors of 70–75% efficiency.
skip to main |
skip to sidebar
Populer
-
What Is a Hybrid System? A hybrid system combines different power sources to maximize each one’s strengths, while compensating for the othe...
-
Factors Influencing Alignment procedure 1- Eccentricity (runout) Check · This might be done by a dial gauge 2- Baseplate of machines (soft...
-
Distillation usually is the most economical method of separating liquids, superior to extraction, adsorption, crystallization,or others. Fo...
-
While research has developed a significant and detailed filtration theory, it is still so difficult to define a given liquid-solid system th...
-
Induced vibration of any system involves the coupling of some exciting forces with an elastic structure. In the case of flow-induced vibrati...
-
Principles To provide the necessary alignment between the diesel engine and all mechanically dri-ven components, an understanding of the typ...
-
Long tube vertical evaporators with either natural or forced circulation are most popular. Tubes are 19–63 mm dia and 12–30 ft long. In for...
-
DISI includes a whole new set of innovations for gasoline engines. To mention a few, direct injection (including cooling the air-gasoline m...
-
Submerged arc welding: (SAW) In submerged arc welding also known as hidden arc welding, submerged melt welding, or sub-arc welding the arc ...
-
The proper use of basic heat-transfer knowledge in the design of practical heat-transfer equipment is an art. Designers must be constantly a...
Copyright © allengineering-info | Powered by Blogger | Template by Blog Go Blog